LDAP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
LDAP
Introduction to LDAP :
LDAP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is a widely used protocol for accessing and managing directory information. When integrated with Active Directory (AD), LDAP serves as the primary means of querying and modifying objects within AD. In this note, we will explore how LDAP works with Active Directory.
LDAP uses port 389, and LDAP over SSL (LDAPS) communicates over port 636.
LDAP Overview:
LDAPis a protocol used to access and interact with directory services, which store and organize information in a hierarchical structure.- It operates over
TCP/IPand uses a client-server model, where the client sends requests, and the server responds with the requested data.
What LDAP is not :
I’d rather want to be sure that you are aware of what LDAP is not:
- LDAP is not a server
- LDAP is not a database
- LDAP is not a network service
- LDAP is not a network device
- LDAP is not an authentication procedure
- LDAP is not a user/password repository
- LDAP is not a specific open or closed source product
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a protocol used for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services, but it is not a server, database, network service, network device, authentication procedure, user/password repository, or a specific open or closed-source product. LDAP is a protocol that facilitates communication between clients and directory servers for directory-related operations.
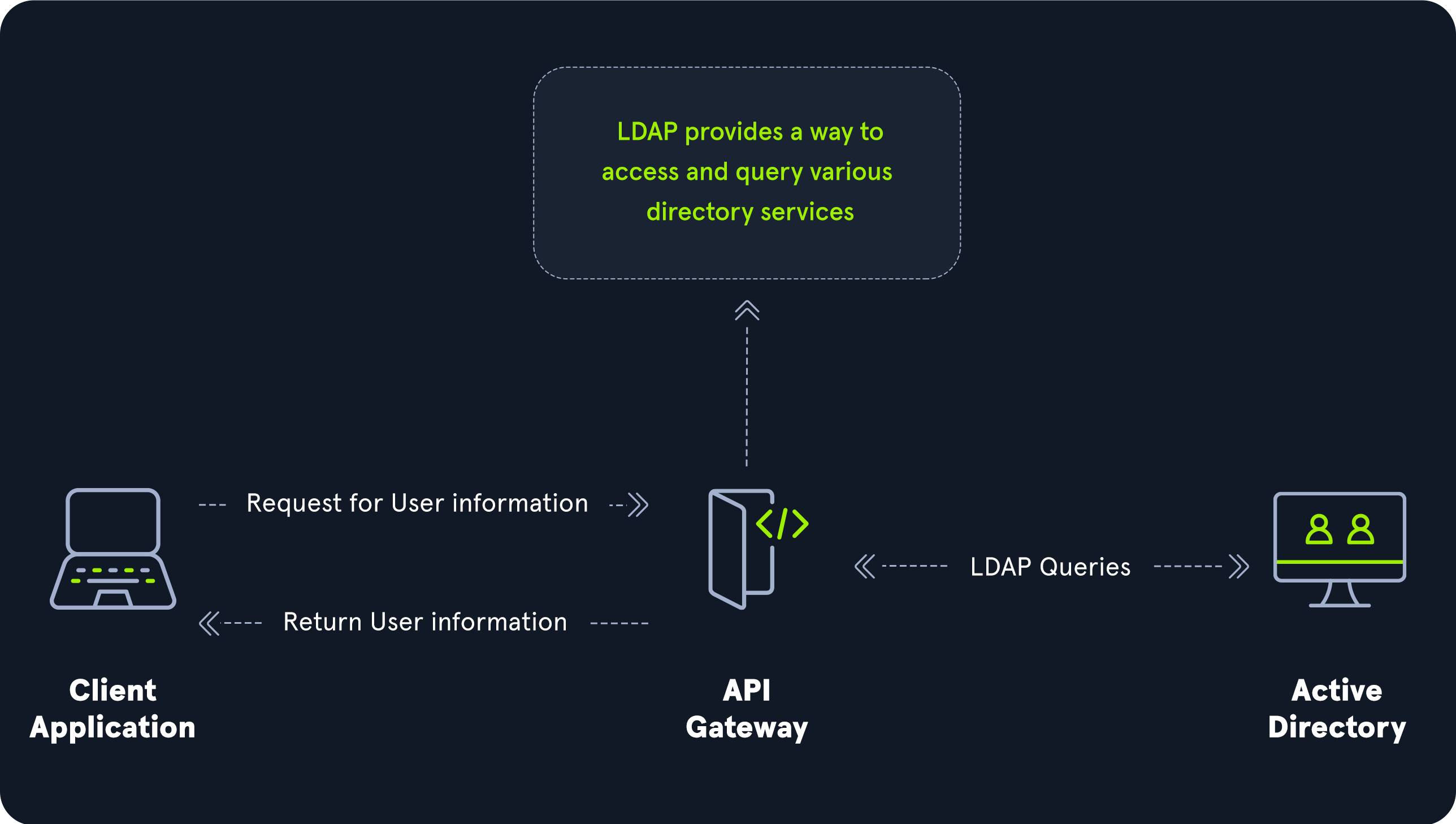
LDAP and Active Directory Integration :
Active Directory is LDAP-compliant, allowing clients to communicate with it using LDAP queries to retrieve, add, modify, or delete information about directory objects.
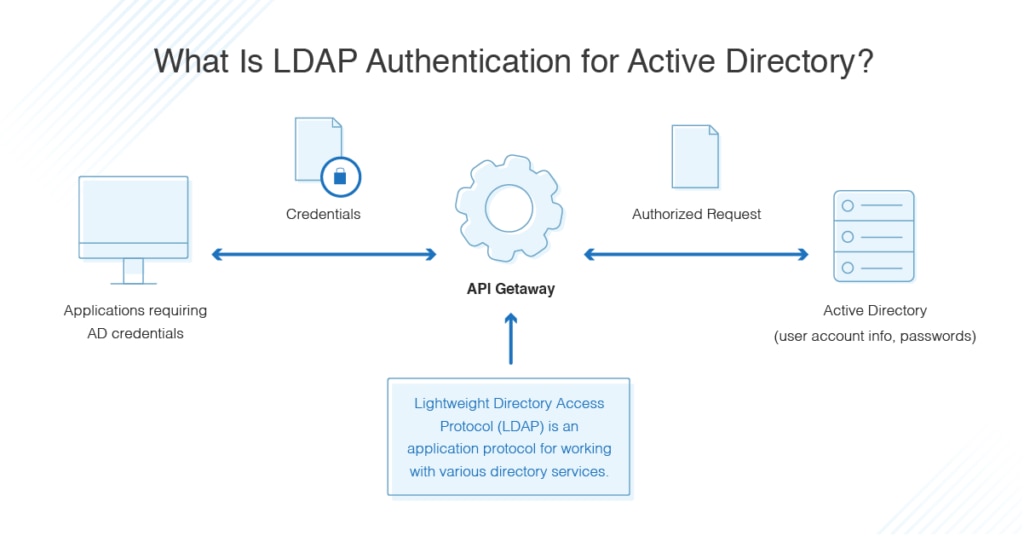
What is LDAP Authentication For Active Directory :
LDAP authentication for Active Directory is a process that verifies user identities by checking their credentials against a directory service, like Microsoft’s Active Directory, using the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). It’s a common method for securing access to network resources in enterprise environments.
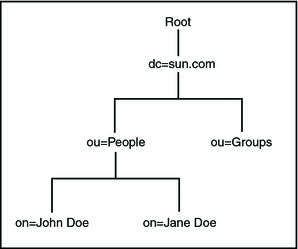
LDAP Distinguished Names (DNs) in AD:
In Active Directory, LDAP Distinguished Names (DNs) uniquely identify and locate entries within the directory tree. DNs are structured hierarchically and typically include components such as the Common Name (CN), Organizational Unit (OU), Domain Component (DC), and more. For example:
1
CN=user,CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com
Here, user is the Common Name within the Users container of the example.com domain. DNs play a crucial role in LDAP queries and operations, helping specify the exact location of directory entries.
The DN includes the object’s ` Relative Distinguished Name (RDN)` and the path from the root of the directory to the object.
LDAP Queries in AD:
LDAP queries are used to search for specific information within Active Directory. a simple example of an LDAP query:
1
(&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName=username))
This query searches for a user object with a specific SAM Account Name (username).
Let’s break it down:
&: Logical AND operator.
(objectClass=user): Specifies that the entry must be a user object.
(sAMAccountName=username): Specifies the SAM Account Name of the user.
You can customize LDAP queries based on your specific search criteria, allowing you to retrieve information about users, groups, or other objects in the Active Directory. The structure and syntax of LDAP queries may vary depending on the requirements of your search.
AD LDAP Authentication:
LDAP BIND TYPES :
in the LDAP protocol the authentication operation is called Bind. A bind can be performed in 3 different ways:
| Bind Types | Credit Requirement |
|---|---|
Anonymous Bind | No |
Simple Password Bind | Yes |
SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer, allowing a larger set of authentication mechanisms) Bind | Yes |
Note : The LDAP standard is defined in a series of documents known as Request for Comments (RFCs), primarily RFC 4510 and its related RFCs.
Simple Authentication :
- Includes anonymous, unauthenticated, and username/password authentication.
- Users provide a username and password in a BIND request to authenticate with the LDAP server.
- This method is straightforward but may transmit passwords in cleartext, posing a security risk.
SASL Authentication:
- SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) utilizes other authentication services like Kerberos for binding to the LDAP server.
- Instead of transmitting credentials directly, SASL sends authentication requests to the authorization service (e.g., Kerberos) using the LDAP protocol.
- The authorization service responds with challenge/response messages, determining successful or unsuccessful authentication.
- SASL enhances security by separating authentication methods from application protocols.
Note : LDAP authentication messages are transmitted in cleartext by default, making them susceptible to interception on the internal network. To enhance security, it is recommended to use TLS encryption or similar methods to protect this information during transit.
LDAP Filter Syntax:
| The LDAP filter defines the conditions that must be fulfilled in order for the Search to match a given entry and must follow the syntax defined in RFC 4515. The filter is composed of assertions that can be joined with AND (&) or OR ( | ) operators, or negated with the NOT (!) operator. The AND, OR, and NOT choices can be used to form combinations of assertions in a complex filter. At least one filter element must be present in an AND or in a OR. |
example :
NOT, AND and OR
mix the NOT, AND and OR to form a more complex filter as in:
1
(|(&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(!(cn=Smith))(cn=admin*))
This filter example retrieves all entries whose cn starts with admin and all entries of class inetOrgPerson with a surname different from Smith.
Read More Here
LDIF (LDAP Data Interchange Format) :
LDIF, or LDAP Data Interchange Format, is a standard plain-text format for representing LDAP directory entries and updates. It provides a way to import and export directory entries, making it a common format for exchanging data between LDAP-compliant directory servers and applications.
In LDIF, each entry or update is represented in a structured and readable manner. Here’s a basic example of an LDIF entry:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
dn: cn=John Doe,ou=Users,dc=example,dc=com
changetype: add
objectClass: person
objectClass: organizationalPerson
objectClass: inetOrgPerson
cn: John Doe
sn: Doe
givenName: John
mail: john.doe@example.com
LDIF is defined in RFC2849 in two different flavours: LDIF-CONTENT and LDIF-CHANGE
- LDIF-CONTENT is used to describe LDAP entries in an ASCII stream (i.e. a file)
- LDIF-CHANGE is used to describe Add, Delete, Modify and ModifyDn operations.
Common LDAP Operations in Active Directory :
Bind: The process of authenticating the client to the LDAP server.Search: The process of querying AD for specific information using LDAP filters.Add: The process of creating new objects in the AD directory.Modify: The process of updating existing attributes of objects in the directory.Delete: The process of removing objects from the directory.
LDAPS and LDAP over TLS :
LDAPS, the secure variant of LDAP, employs SSL/TLS encryption to safeguard data during transmission. Within Active Directory, LDAPS is fully supported, providing a secure channel for the exchange of sensitive information, reinforcing the confidentiality and integrity of your data.
LDAP over SSL (LDAPS) :
Protocol: LDAPS secures LDAP communication using the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Port: LDAPS typically operates on port 636, ensuring encrypted communication.
Encryption: Data exchanged between the LDAP client and server is encrypted, guaranteeing both confidentiality and integrity.
Usage: LDAPS is the go-to choice when a secure and encrypted connection is required right from the beginning of the LDAP session.
Example LDAPS URL:
1
ldaps://ldap.example.com:636
LDAP over TLS (STARTTLS):
Protocol: LDAP over TLS introduces security through the STARTTLS operation, allowing the establishment of a secure connection within a plain LDAP session.
Port: Initially, the standard LDAP port (usually 389) is used, with encryption negotiated using STARTTLS.
Encryption: The connection begins in an unencrypted state but transitions to a secure, encrypted one after the STARTTLS operation.
Usage: STARTTLS is particularly useful when there’s a need to upgrade a plain LDAP connection to a secure one during the session.
Example LDAP over TLS URL:
1
ldap://ldap.example.com:389
Both LDAPS and LDAP over TLS play crucial roles in fortifying LDAP communication security, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive directory information.
Conclusion:
LDAP is a powerful protocol that allows clients to interact with directory services like Active Directory efficiently. By understanding LDAP’s basic principles and its integration with Active Directory, administrators and developers can effectively manage and query directory information, providing a robust and secure directory service for Windows-based networks.