Kerberos Active DIrectory
Kerberos
Introduction:
What is Kerberos protocol :
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol designed to provide secure authentication for users and services in a distributed computing environment. It is primarily used to ensure that only trusted entities can access network resources and services. Kerberos uses tickets to authenticate users without transmitting their passwords over the network, making it a more secure authentication mechanism.
Kerberos and active directory :
Kerberos and Active Directory (AD) are integral components of modern network authentication and security. Kerberos is a network authentication protocol, while Active Directory is a directory service developed by Microsoft. Together, they provide a robust and secure authentication and authorization framework for users and resources in a Windows domain-based network environment. In this note, we will explore the key features of Kerberos and its integration with Active Directory.
The Kerberos protocol uses port 88 (both TCP and UDP). When enumerating an Active Directory environment, we can often locate Domain Controllers by performing port scans looking for open port 88 using a tool such as Nmap.
Components of Kerberos:
Principal :In Kerberos, users, services, and servers are represented as principals. A principal is a unique identifier associated with a user or service.Authentication Server (AS) :The AS is responsible for initial authentication. When a user wants to access a service, they request a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) from the AS by providing their credentials (username and password).Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) :The TGT is a time-limited ticket issued by the AS to the client after successful authentication. It allows the client to request service tickets without re-authenticating repeatedly.Ticket Granting Service (TGS) :The TGS is responsible for issuing service tickets to the client. To obtain a service ticket, the client presents the TGT to the TGS.
• Service Ticket : The service ticket is issued by the TGS to the client, granting access to a specific service.
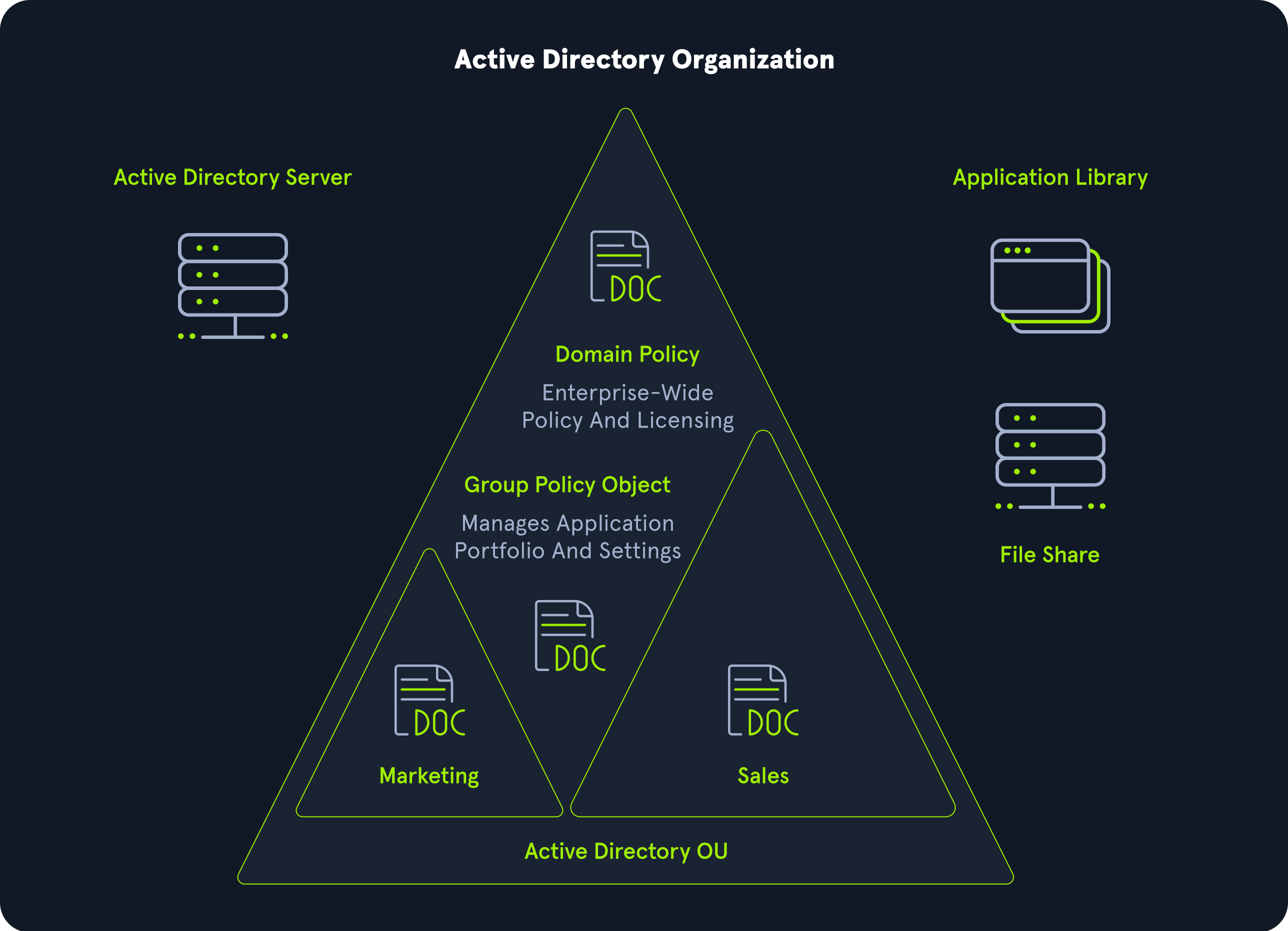
Active Directory (AD):
AD is Microsoft’s implementation of a directory service that centralizes and manages network resources such as user accounts, computers, printers, and other network devices. It provides a hierarchical database that stores information about the network objects.
Integration of Kerberos with Active Directory:
Active Directory uses Kerberos as its default authentication protocol. When a Windows client joins an AD domain, it automatically becomes a part of the Kerberos realm. The AD domain controllers act as the Authentication Servers (AS) in the Kerberos infrastructure.
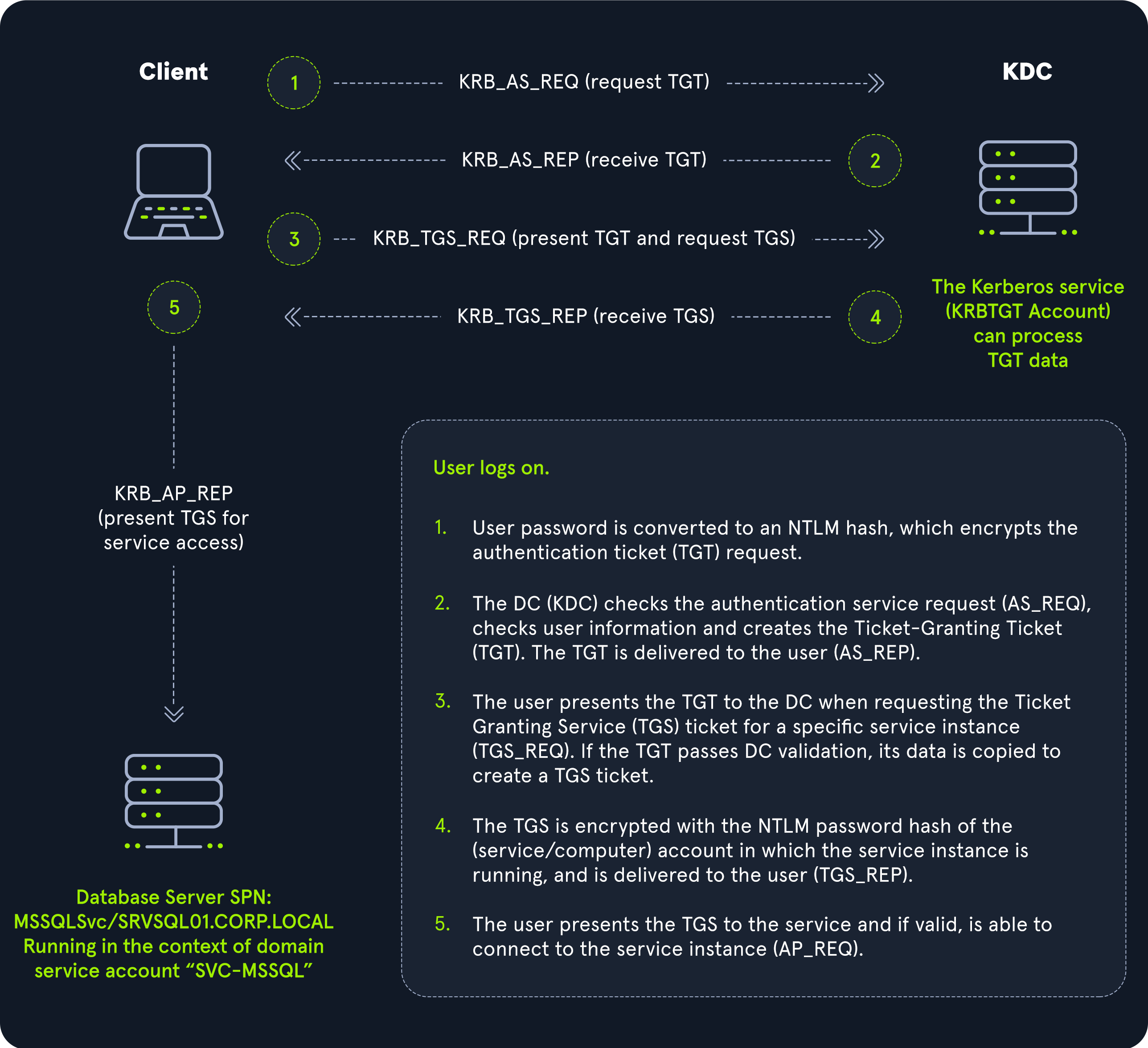
Kerberos Authentication Process in Active Directory:
- The user logs on, and their password is converted to an
NTLM hash, which is used to encrypt theTGT ticket. This decouples the user’s credentials from requests to resources. - The
KDC serviceon theDCchecks theauthentication service request (AS-REQ), verifies the user information, and creates aTicket Granting Ticket (TGT), which is delivered to the user. - The user presents the
TGTto theDC, requesting aTicket Granting Service (TGS)ticket for a specific service. This is theTGS-REQ. If the TGT is successfully validated, its data is copied to create aTGSticket. - The TGS is encrypted with the
NTLMpassword hash of the service or computer account in whose context the service instance is running and is delivered to the user in theTGS_REP. - The user presents the TGS to the service, and if it is valid, the user is permitted to connect to the resource (AP_REQ).
Authentication Service Request :AnAS-REQis a message sent to theauthentication service (AS). All the AS does is exchange credentials for tickets. These credentials can be anything, but are often passwords.
Benefits of Kerberos with Active Directory:
Single Sign-On (SSO) :Kerberos enablesSSO, allowing users to access multiple services with a single authentication, enhancing user experience and reducing the need to remember multiple passwords.Mutual Authentication :Both the client and the server mutually authenticate each other through cryptographic mechanisms, ensuring the authenticity of the communication.No Password Transmission :Kerberos avoids transmitting user passwords over the network, significantly reducing the risk of password interception.Ticket Expiration:Tickets have a limited validity period, minimizing the impact of compromised tickets.
Conclusion:
Kerberos and Active Directory play crucial roles in securing authentication within Windows-based network environments. By using the robust and proven Kerberos protocol, Active Directory provides a strong foundation for ensuring secure access to network resources, protecting sensitive data, and enhancing overall network security. Understanding the principles of Kerberos and its integration with Active Directory is essential for network administrators and IT professionals tasked with maintaining a secure and efficient network infrastructure.